The Secret Of Info About Depreciation Expense On A Balance Sheet View Company Financial Statements

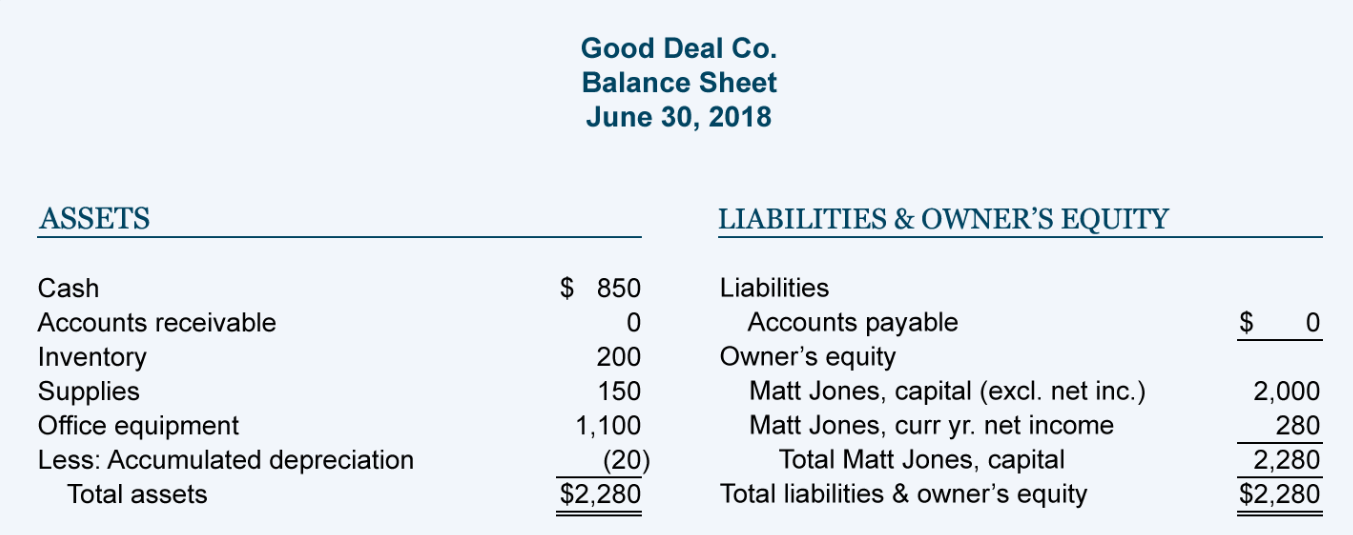
Balance sheet (under assets, but typically shown as a deduction from the building's gross amount).
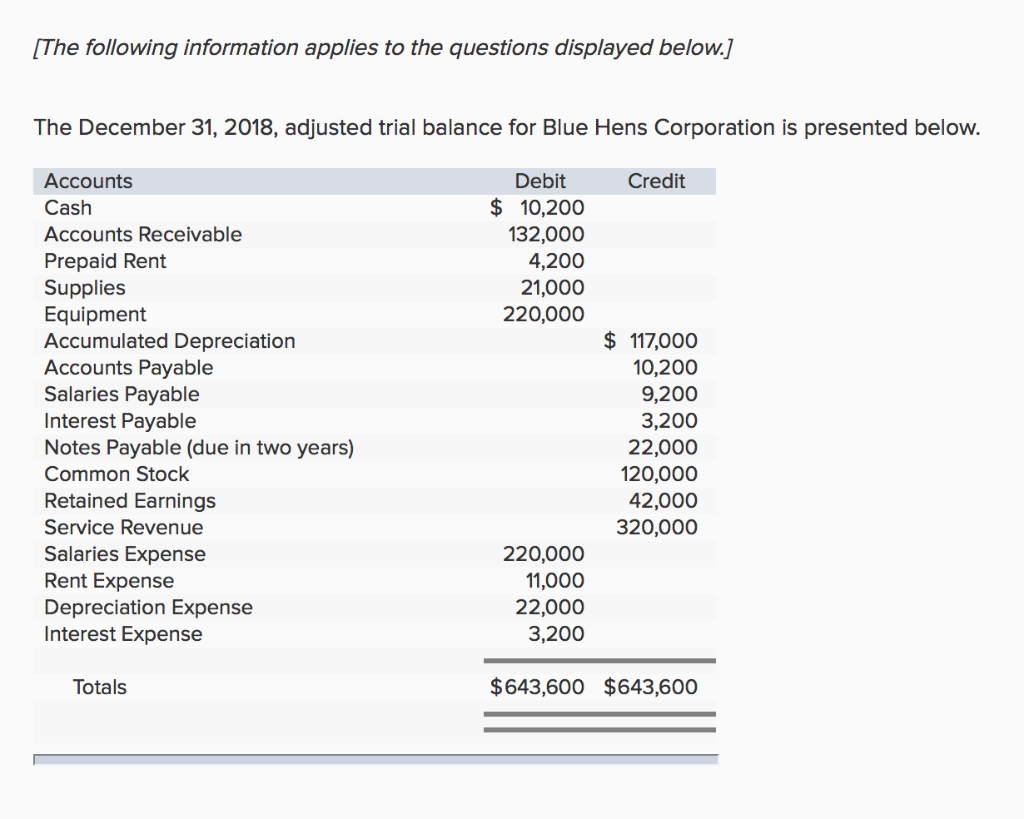
Depreciation expense on a balance sheet. Depreciation expense refers to the decrease in value of an asset over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence or Sep 14, 2021 • 4 min read. The cost for each year you own the asset becomes a business expense for that year.
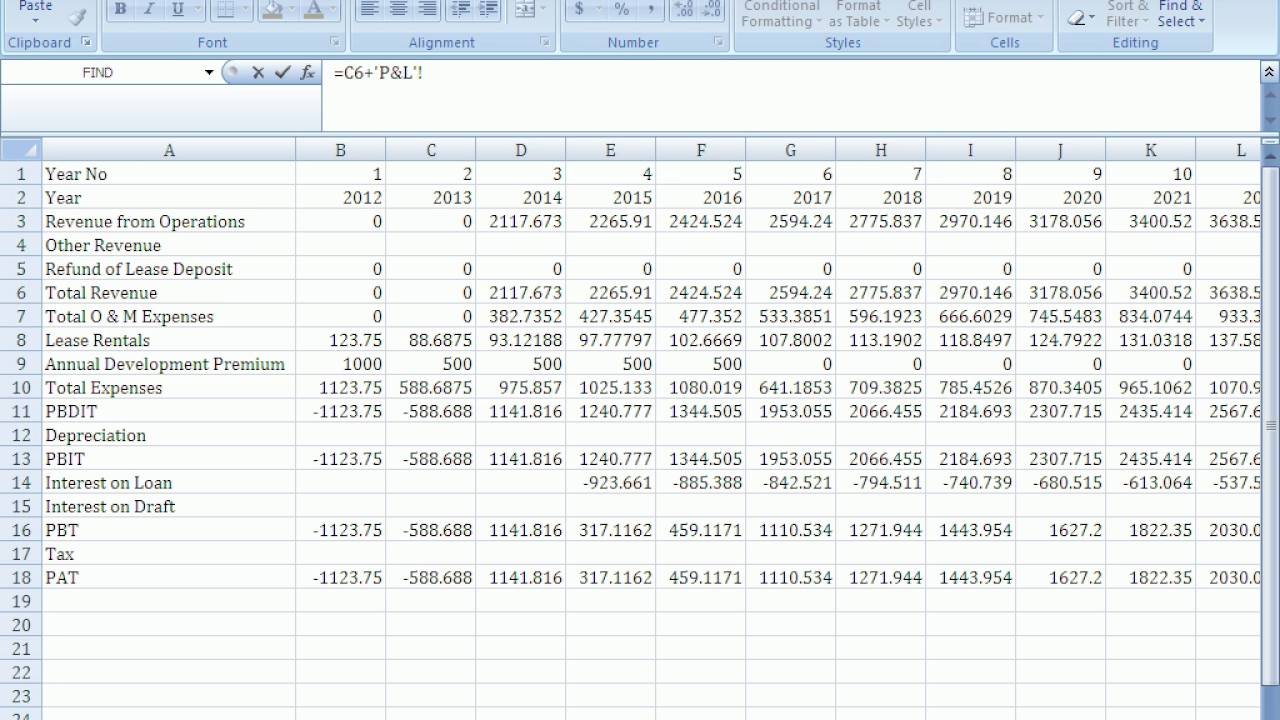
As a business owner or financial analyst, it is crucial to understand the concept of depreciation expense and its impact on your company's balance sheet. It accounts for depreciation charged to expense for the income reporting period.
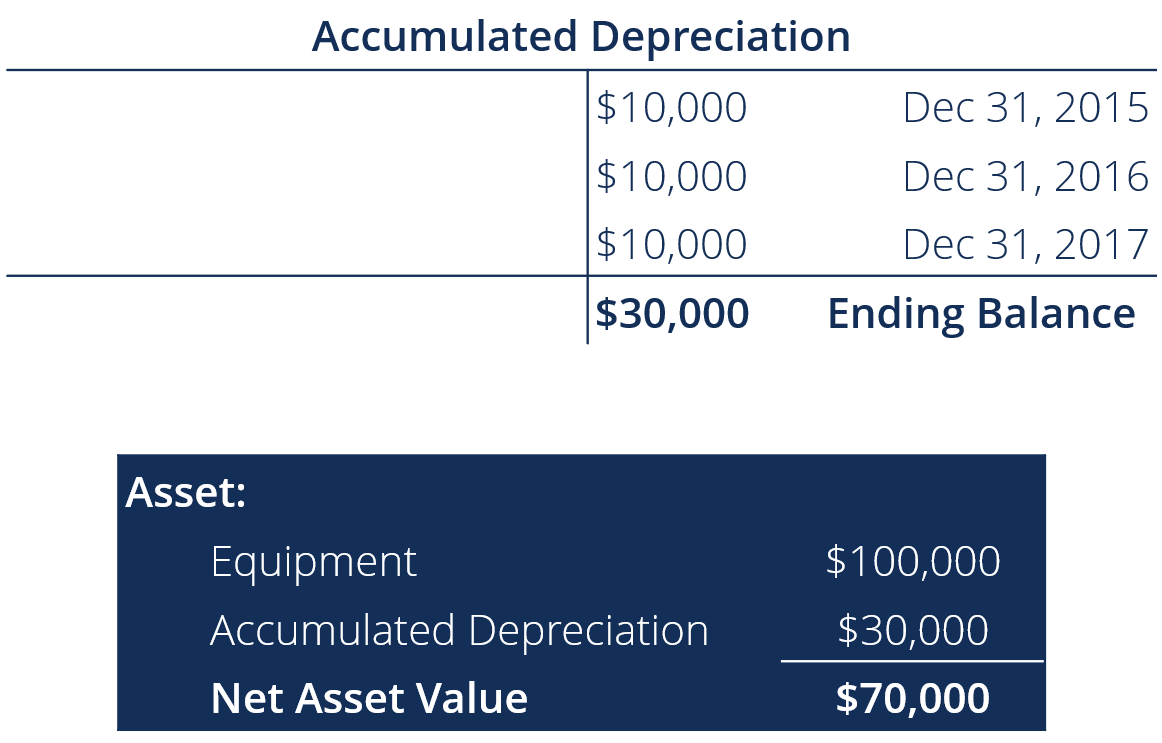
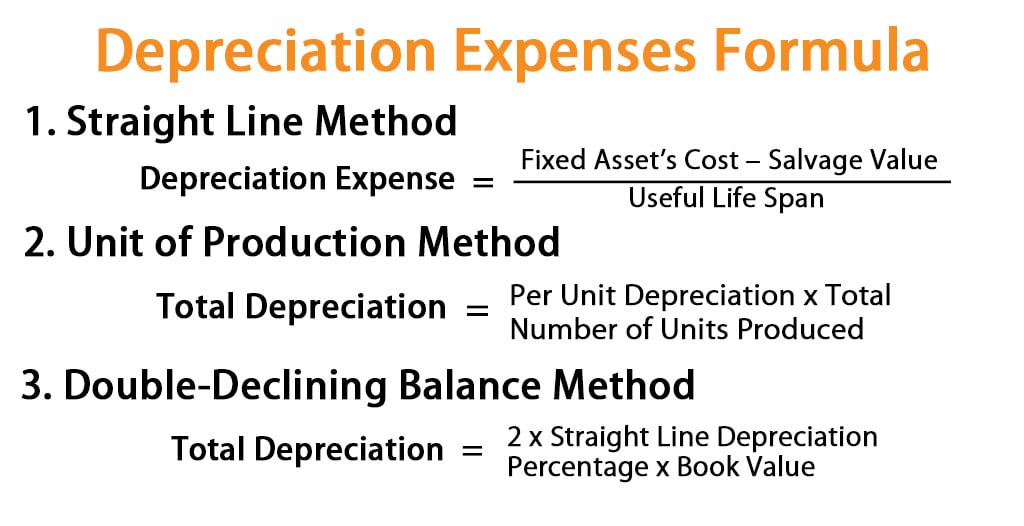
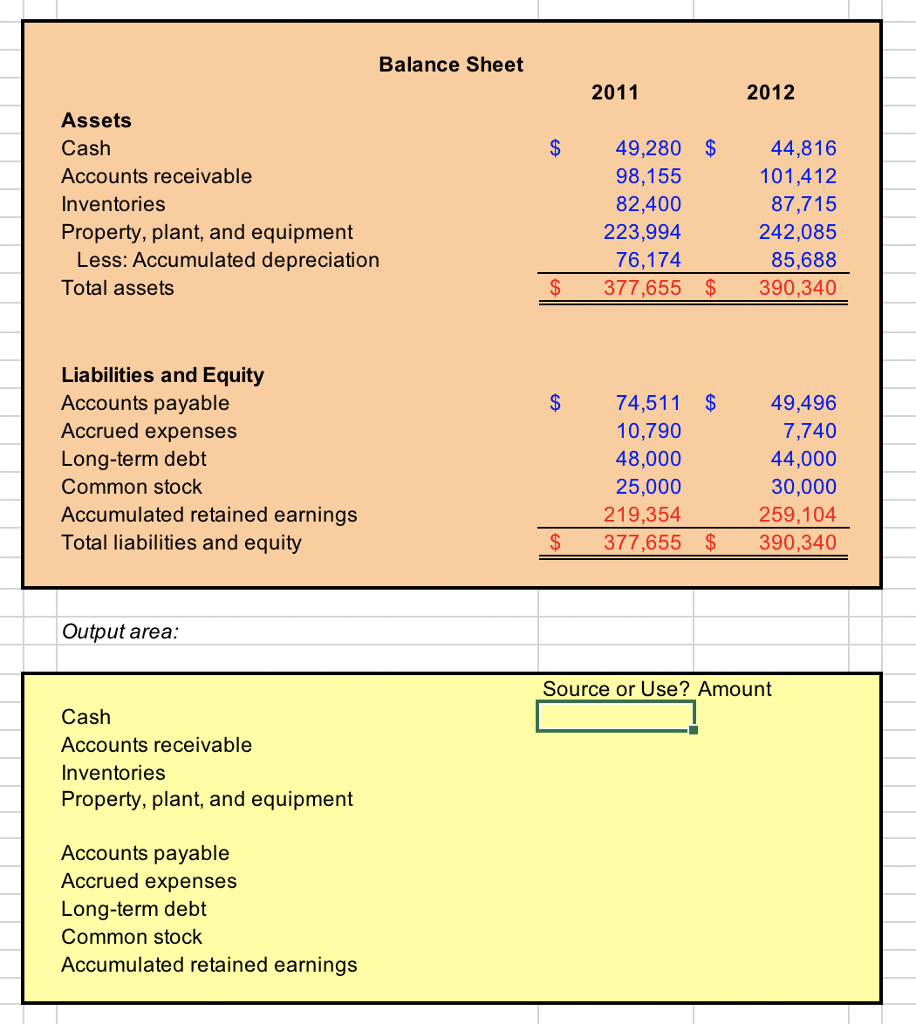
Showing contra accounts such as accumulated depreciation on the balance sheets gives the users of financial statements more information about the company. The formula for this is (cost of asset minus salvage value) divided by useful life. Accumulated depreciation is calculated by taking the initial cost of an asset and subtracting the total depreciation expense recorded to date.
Fixed assets lose value over time. As you see, cash is not involved. After the first year, your car would be shown on the balance sheet at the purchase price of $40,000 minus $8,000.
This means that it is a deduction from revenue on the income statement that reduces the level of reported income. Depreciation expense is the amount that a company's assets are depreciated for a single period (e.g, quarter or the year), while accumulated depreciation is the total amount of wear to date. The accumulated depreciation would total $112,500 at the end of five years, equaling $22,500 per year x 5 years.
For example, if you buy a car for $40,000 and expect it to last for five years, you might depreciate it at $8,000 per year. It estimates that the salvage value will be $4,000 and the asset's useful life, 15 years. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the concept of depreciation and its significance on financial statements.
In most cases, fixed assets carry a debit balance on the balance sheet, yet accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, since it offsets the value of the fixed asset (pp&e). Accumulated depreciation is not recorded separately on the balance sheet. This can result in a temporary difference between the depreciation expense claimed for tax and accounting purposes, which may generate a deferred tax asset.
Is depreciation expense on the balance sheet? Or why that classification eve. vantage virtual services | small business bookkeeping on instagram: On walmart’s balance sheet, each year, it will add $22,500 to its accumulated depreciation.
The income statement books a depreciation expense of $9,000 during the initial year. The depreciation expense per year would be $4,400. Depreciation expense is recorded on the income statement as an expense or debit, reducing net income.
Depreciation expense has a direct impact on the balance sheet through the following components: This method is used to calculate the amount of depreciation expense that will be recorded on the balance sheet for each year of the asset’s life. Depreciation is a financial accounting method used to allocate the cost of tangible assets over t. clearias on instagram:



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Why_is_Accumulated_Depreciation_a_Credit_Balance_Jul_2020-01-34c67ae5f6a54883ba5a5947ba50f139.jpg)